 | Can You Name |
- How does endocrine system control differ from nervous system control?
- Review how endocrine glands are different from exocrine glands. What is a neuroendocrine gland and give examples?
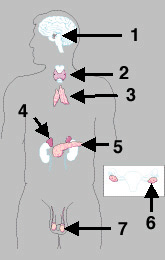
- Name and locate each endocrine gland. Be familiar with the histology of each gland. (lab)
- Name 4 organs that secrete hormones but are not exclusively endocrine glands.
- Define hormone. List the three major classes of hormones and give examples of each one.
- What are the major factors that determine how a hormone communicates with its target cell?
- Define target cell. Describe the 5 ways a hormone may work to alter their target cells activities.
- Which signaling effect is used by almost all amino acid based hormones?
- Briefly outline the steps of the second messenger system called the Cyclic AMP Signaling Mechanism. Include these terms: first messenger, G protein, GTP, adenylate cyclase, second messenger, cyclic AMP and protein kinases.
- G Protein Animation
G Protein Animation- Explain the concept of amplification. Why is phosphodiesterase important?
- Which hormone uses the PIP - Calcium Signal Mechanism second messenger system? Briefly outline the steps of this second messenger system. Include these terms: G-protein, phospholipase, PIP2, DAG (diacylglycerol), IP3, action of calcium, and calmodulin.
- PIP-Calcium Signal Mechanism Animation
PIP-Calcium Signal Mechanism Animation- Briefly outline the direct gene activation process used by steroid hormones.
- Animation of Steroid Hormones
Animation of Steroid Hormones- What is the most important factor in target cell activation? What three other factors are also important to target cell activation?
- What are the three types of hormone interaction?
- Describe the three types of stimuli that affect endocrine glands. Give an example for each type.
- How is the nervous system important in modifying the endocrine system?
- Describe the location of the pituitary (hypophysis), its lobes and their functions.
- What is the hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract and why is it important? Where does the track start and what is produced there? Where does the tract end?
- Animation of Hormonal Connection of Posterior Pituitary and Hypothalamus
- Describe the parts of the hypophyseal portal system. Where is it located and why is this connection important? What is the significance of releasing and inhibiting hormones?
- What is a tropic hormone? Give four examples and what gland releases them?
- Describe the direct effect of Growth hormone (GH).
- Describe the indirect action of Growth hormone (GH) on growth. Include IGF’s.
- Explain the direct effects of GH on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. What is the diabetogenic effect?
- What controls the secretion of Growth hormone (GH)? What are the effects of hypo and hypersecretion of GH in children? Effects of hypersecretion in adults?
- List the other hormones of the Adenohypophysis, their target organs; effects and regulation (See table 15.1, page 532).
- Animation of Adenohypophysis Hormones
- Where are the two hormones stored by the neurohypophysis? Where are these hormones synthesized? What causes their release from storage?
- Describe the target organs, effects and regulation of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH). What the effects of hypo and hypersecretion of ADH? (See table 16.1).
- Describe the target organs, effects and regulation of Oxytocin (OT). What the effects of hypo and hypersecretion of OT? (See table 16.1).
- Describe the thyroid gland: lobes, isthmus, follicles, thyroglobulin and colloid.
- Describe the 5 main effects of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 (Thyroxine). Include the Calorigenic Effect.
- Describe the major feedback mechanisms affecting thyroid secretion.
- Animation of Feedback System
- Describe the four major thyroid disorders and their causes.
- Which cells produce Calcitonin (CT)? What are the target organs, effects and regulation for CT?
- Where are the parathyroid glands located? Which cells secrete PTH?
- What are the target organs, effects and regulation of PTH?
- Why is the adrenal gland considered a two endocrine gland? What common function do all adrenal gland hormones have?
- List the zones of the adrenal cortex. Which hormones are secreted from each zone?
- Describe the general functions of the Mineralocorticoids. Which Mineralocorticoid is most potent? What stresses cause aldosterone’s release? What is aldosterone’s target organ?
- Describe how the Renin-Angiotensin mechanism regulates aldosterone secretion.
- Describe how the Atrial Natriuretic Peptide regulates aldosterone secretion.
- Describe the actions of glucocorticoids. What stressors elevate the levels of glucocorticoids?
- How are excessive amounts of glucocorticoids a problem?
- Describe Addison’s and Cushing’s diseases and their causes.
- List the hormones of adrenal medulla. How are chromaffin cells unusual and what do they secrete? What is the role of these hormones in response to short term stress?
- Describe the roles of the pancreatic acinar cells, pancreatic islets (Islets of Langerhans), alpha cells and beta cells.
- List the effects of glucagon. What is the stimulus for its secretion? Why is this called the hyperglycemic hormone?
- List the effects of insulin. What are the stimuli for the secretion of insulin? Why is this called the hypoglycemic hormone?
- Describe the symptoms of diabetes mellitus: Polyuria, polydipsia and polyphagia. What are ketones and what is their significance in diabetes mellitus?
- List the hormones produced by the gonads.
- What hormone is produced by the pineal gland? What is its main function?
- What are the secretions of the thymus gland? What is their function?
- Review Quiz Glands and Hormones