HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
JOURNAL QUESTIONS
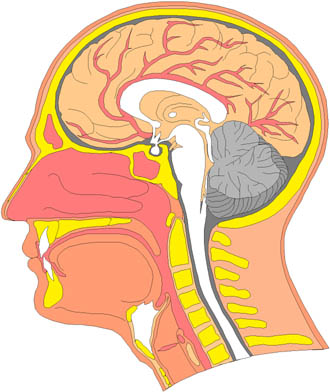

- List the four main functions of the spinal cord.
- Section 13.1 Surface anatomy, Meninges, Cross Sectional Anatomy. These terms are covered in the Must Know Lab Book
- Define ascending tracts of the spinal cord.
- Define descending tracts of the spinal cord.
- Define decussate. What is the consequence of decussation (crossing-over)?
- Recognize these tracts as ascending; Gracile fasciculus and Spinothalamic and know each tracts specific function. (See Table 13.1)
- Recognize these tracts as descending; Corticopsinal and Reticulospinal and know each tracts specific function. (See Table 13.1)
- Describe the structure of a nerve.
- Review spinal nerve structures from the Must Know Lab Book.
- Define endoneurium, fascicle and perineurium.
- Describe the three types of nerve fibers; sensory nerves, motor nerves and mixed nerves.
- Describe the structure and location of a ganglion.
- Section 13.2 Spinal nerves, proximal branches, distal branches, nerve plexuses. These terms are covered in the Must Know Lab Book
- Review the major nerves associated with each plexus in the Must Know Lab Book.
- Define reflex and explain why we have them. List four important properties of a reflex.
- Define Somatic reflexes.
- Describe the five components of a reflex arc.
- Describe a withdrawal reflex and the stimulus that initiates it.

- Describe the three major portions of the brain; cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem.
- Describe the arrangement of the brainís gray and white matter. Define cortex, nuclei and tracts.
- Review the three meninges that surround the CNS.
- Contrast the dura of the brain and the spinal cord.
- Define dural sinus (superior sagittal sinus) and describe its function.
- Define and locate ventricles and their interconnections.
- Describe the choroid plexuses their location and function.
- Describe the Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF); its location, production and composition. Review the role of ependymal cells.
- Trace the path of CSF from production to circulation to re-absorption. (See figure 14.7)
- Name 2 structures of the blood brain barrier and explain the barrierís importance. List some substances that can and cannot pass through the barrier.
- List the fundamental sensory and motor functions of the medulla oblongata.
- Describe the location and action of the cardiac center, vasomotor center and respiratory centers.
- Briefly describe the medulla pyramids and general function lost if they are severed.
- Describe the pons and its functions.
- Describe the function of the brainstem regions: midbrain, cerebral peduncles, corpora quadrigemina and red nucleus.
- Describe the location and functions of the reticular formation.
- Describe the functions of the cerebellum.
- List the structures found in the diencephalon. Describe the function of the thalamus, hypothalamus and pineal gland.
- Define cerebrum, cerebral hemispheres, corpus callosum, gyrus, sulcus and fissure.
- Review the location of the lobes of the cerebrum. List the functions of each.
- Describe the white matter of the cerebrum. Briefly describe the projection, commissural and association tracts.
- Define and describe the cerebral cortex
- Describe the basal nuclei and their functions.
- List the parts and functions of the Limbic System
- Briefly describe the steps of sleep and their relationship to brain waves.
- Define association area. Describe association functions disrupted in the frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobes when there is a cerebral lesion (injury)
- Describe the role of the hippocampus in memory.
- Identify brain regions concerned with emotion. Describe each regionís specific role.
- Identify the lobes of the cerebrum concerned with senses. Describe the role of the primary sensory cortex.
- Describe the location of the special sensory areas for vision, hearing, taste and smell.
- List the names and location of the general senses. Describe the location and role of the Postcentral gyrus.
- Give the location and function of the motor association (Premotor) area and primary motor area.
- Describe the location and function of the two language areas; Wernicke and Broca
- Define cerebral lateralization. List the functional differences between the right and left hemispheres.
- For each cranial know how to identify it by name and number. Know where each cranial nerve originates.
- Describe the functions of each cranial nerve. Identify each as sensory, motor or mixed. (See table 14.1)
Chapter 15:
Autonomic Nervous System & Visceral Reflexes
- List the effectors and several effects of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Describe visceral reflexes controlled by the ANS
- List the two divisions of the ANS. Match the terms Flight or Flight and Resting and Digesting with the division of the ANS they represent.
- Compare the functional differences of the two divisions.
- Describe how the motor neuron arrangement of Somatic Nervous System and Autonomic Nervous System differ.
- Define preganglionic and postganglionic fibers.
- Describe why the Sympathetic division is also called Thoracolumbar.
- Describe the structure and location of the Sympathetic Chain of ganglia (Paravertebral).
- Trace the beginning and end of the pre and post ganglioinc fibers in the Thoracolumbar division.
- Explain how the adrenal medulla of the adrenal gland is unusual in its preganglionic fiber arrangement.
- Describe why the Parasympathetic division is also called Craniosacral.
- Name and describe the ganglia in the Parasympathetic division
- Trace the beginning and end of the pre and post ganglioinc fibers in the Craniosacral division
- Name the cranial nerve that carries most of the Parasympathetic flow. List the organs that it affects
- Name the two neurotransmitters released by the Autonomic Nervous System.
- Define and list cholinergic and adrenergic fibers.
- List the two classes of receptors for Acetylcholine (ACh). Describe the location and action of nictotinic and muscarinic receptors.
- List the two classes of receptors for Norepinephrine (NE). Describe the location and action of alpha and beta receptors.



